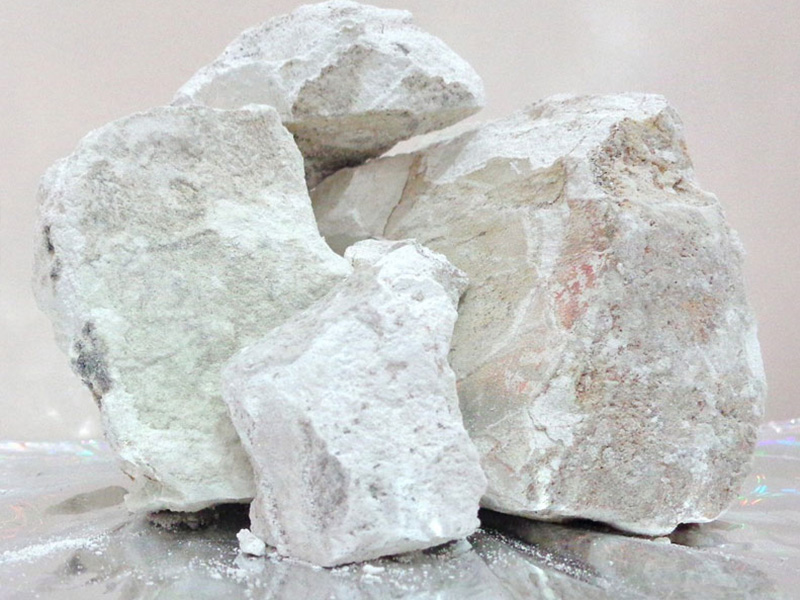
Ideally, dolomite is made of Ca2+ and Mg2+ equal ions that have been separated in order by CO+. A good ordered formation of dolomite will cause some kind of ultra-structural reflections in X-ray Diffractometer (XRD), which is somehow structurally different with calcite.
Most of the present dolomites have a lower order degree in comparison with older ones. “Protodolomite” is made for Ca-Mg carbonates that have been introduced in the laboratory with a very low/no reflection order. Fe replacement in dolomites is frequent and Fe-contained dolomite is being formed with a few FeCO3 percentages, which may follow with Ankrite. Primary dolomite: The word “primary” is mostly applied for a kind of dolomite that refers to the direct sedimentation of sea or lake water. In fact, most of the dolomites are being made through replacement in carbonated minerals that have been formed before. However, dolomite cements are also available. Classification of carbonated stones as per dolomite content: • Limestone: A kind of stone containing 0-10% dolomite. • Dolomite Limestone: A stone containing 10-50% dolomite. • Calcined Dolomite: A stone containing 50-90% dolomite. • Dolostone: A stone containing 90-100% dolomite. Calcined Dolomite is being made through burning dolomite stone under 800-1100°C such that it has minimum 2:30-3 hours stability under 1000°C. Sintering dolomite: This kind of dolomite is being made through burning dolomite stone under 1650-1800°C and is applied for the production of refractory bricks and dolomite mortars. Owning four kiln sets, Azar Sepeed Sepahan Co. has been recognized among the main producers.