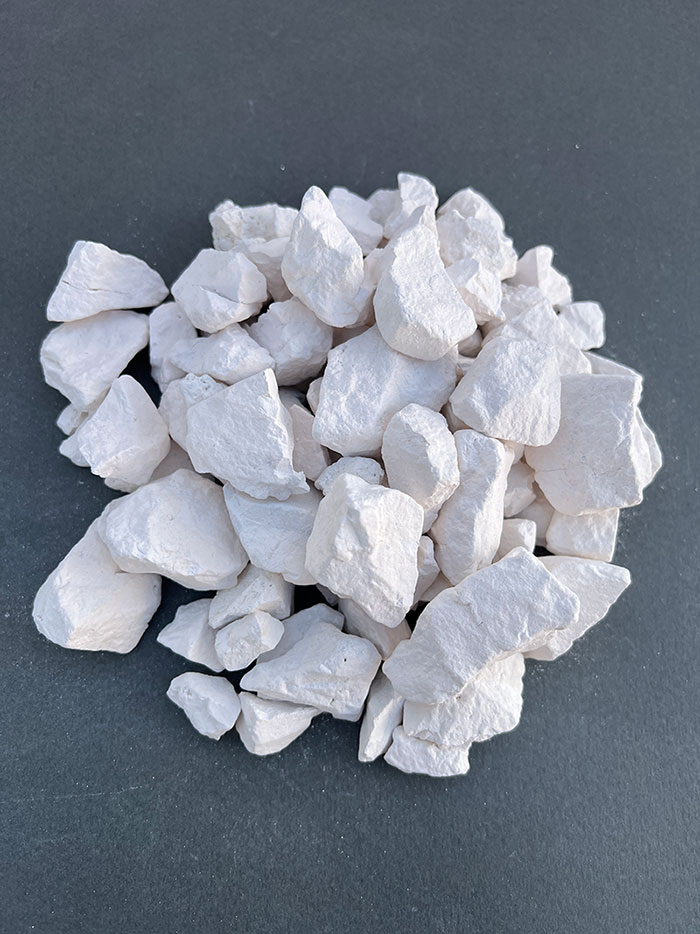
Dolomite is a mineral with the chemical formula CaMg(CO3)2, exhibiting perfect cleavage in three directions. It's commonly found in creamy-gray and grayish-white, but can also be white, yellow, green, or black. Rocks containing dolomite are called dolomite or dolomitic limestone. Carbonate minerals include calcite, aragonite, and dolomite.
Calcination is a process in materials science and chemistry involving heating a material to induce pyrolysis, remove moisture, form intermediate compounds, or carry out solid-state reactions. Simply put, it's the removal of carbon dioxide from a carbonate rock. In the case of dolomite, heating in a furnace at a specific temperature removes impurities. Calcined dolomite, resulting from high-temperature heating of dolomite rock, is primarily composed of magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium oxide (CaO).
Calcined dolomite begins to calcine around 600°C and is fully decomposed into MgO and CaO, with complete CO2 removal, at approximately 900°C. This fully calcined product is also known as "Doloma." It plays a significant role in the steel industry as a slag conditioner and a protective agent for refractory linings. It also finds applications in agriculture as a soil conditioner and in water treatment for environmental purposes.
analysis :
Chemical analysis Calcined Dolomite table
|
Grain Size (mm) |
Bulk Density (gr/cm3) |
L.O.I |
AL2O3 |
Fe2O3 |
CaO |
SiO2 |
MgO |
Chemical Analysis (%) Brand |
Product Name |
|
0 - 50 |
0.9 – 1.5 |
1 – 3 |
0.1 – 0.3 |
0.3 – 0.9 |
52 - 55 |
0.5 – 1.5 |
35-39 |
AZ.C.L.D (DOLOMITE) |
Calcined |

 FA
FA  EN
EN  AR
AR 
