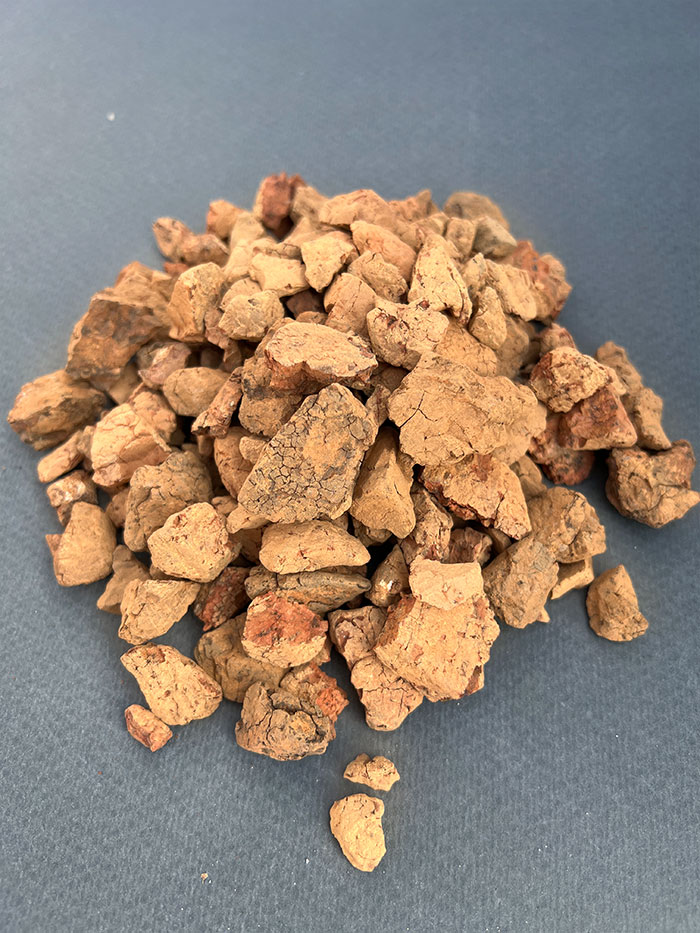
Dunite is named after Dun Mountain near Nelson, New Zealand, where it was first prominently exposed and recognized for its unusual composition. Sometimes called "olivinite," dunite is an ultramafic rock, meaning it is very low in silica (less than 45%) and rich in magnesium and iron. This characteristic makes it a hard and durable rock, highly resistant to chemical and physical weather due to its strong mineral composition.
Despite its abundance in the Earth's mantle, dunite is a rare rock at the surface, making it a geologically interesting composition.
This carbon-neutral and highly versatile rock has many valuable applications, ranging from blast furnace flux and foundry sand and refractory materials to blast cleaning, mineral wool, and environmental applications.
Chemical analysis Dunite Product
|
Grain Size (mm) |
Bulk Density (gr/cm3) |
Cr2O3 |
K2O |
Na2O |
L.O.I |
TiO2 |
AL2O3 |
CaO |
Fe2O3 |
SiO2 |
MgO |
Chemical Analysis (%)/ Brand |
Product Name |
|
0 - 15 |
3.1 – 3.2 |
0.3 – 0.5 |
Trace |
Trace |
Trace |
Trace |
0.6 – 0.8 |
1.4 ± 1.6 |
9 ± 1 |
43 ± 2 |
45 ± 2 |
AZ. Dunite
|
Dunite Sintering |

 FA
FA  EN
EN  AR
AR 
