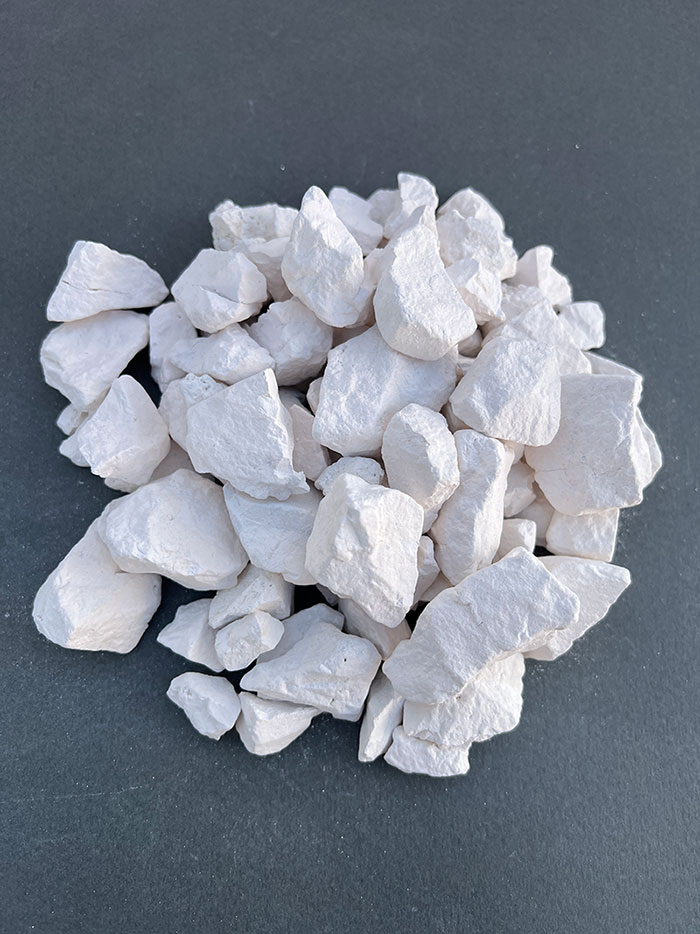
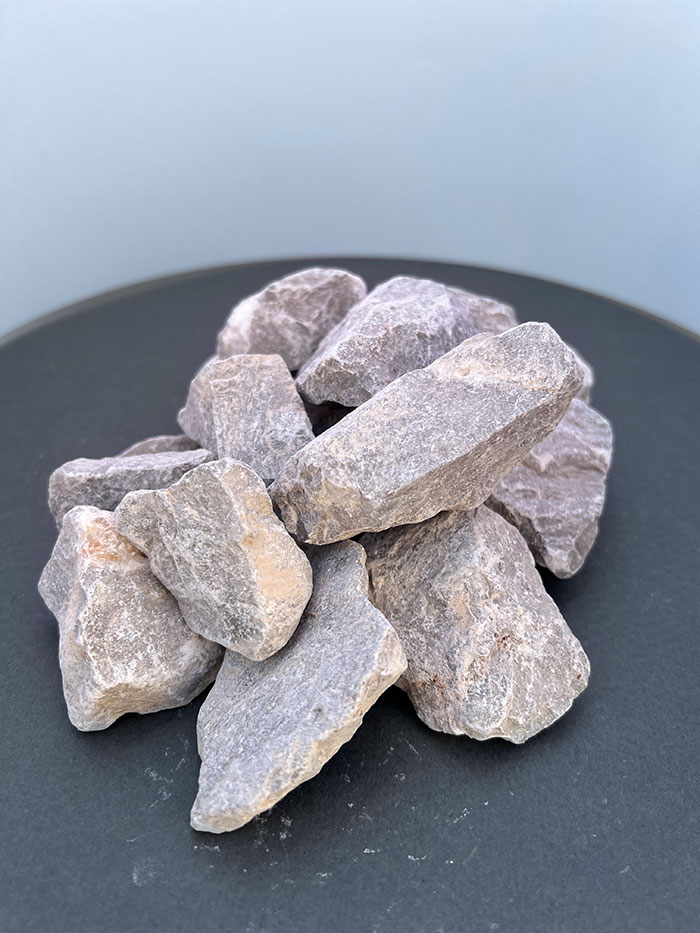
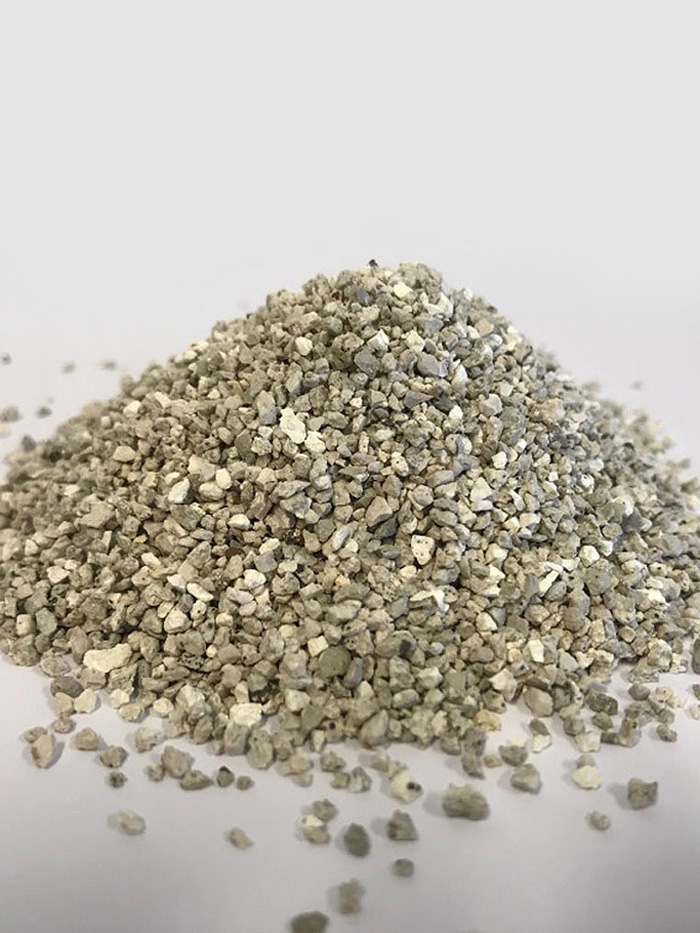
Calcined Products
Calcined Dolomite Production Process:
- Mining: Dolomite, limestone, or magnesite ore is extracted from mines.
- Crushing and Grinding: The raw ore is crushed and ground into smaller pieces.
- Preheating: The crushed ore is preheated in rotary kilns or vertical kilns.
- Calcination: The preheated dolomite ore is calcined at high temperatures (typically between 700 and 900 degrees Celsius).
- Cooling: The calcined products are cooled and processed into powder or granules.
Quicklime is typically derived from limestone or limestone, which are natural sources of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) and calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO₃)₂), respectively.
Calcined lime (burnt lime) is produced by calcining limestone (CaCO3). Calcination is the process of removing CO2 from limestone. Heating limestone to approximately 1200°C yields calcium oxide, also known as quicklime (CaO). In domestic production, less than 3 million tons of limestone are used in the metallurgical industry, with about half consumed in steel production.
Calcined magnesium, also known as (CCM), is a highly reactive form of magnesium oxide (MgO) produced by burning natural magnesium carbonate (magnesite) at temperatures between 800°C and 1500°C.
Dunite is named after Dun Mountain near Nelson, New Zealand, where it was first prominently exposed and recognized for its unusual composition. Sometimes called "olivinite," dunite is an ultramafic rock, meaning it is very low in silica (less than 45%) and rich in magnesium and iron. This characteristic makes it a hard and durable rock, highly resistant to chemical and physical weather due to its strong mineral composition.
Dolomite is a mineral with the chemical formula CaMg(CO3)2, exhibiting perfect cleavage in three directions. It's commonly found in creamy-gray and grayish-white, but can also be white, yellow, green, or black. Rocks containing dolomite are called dolomite or dolomitic limestone. Carbonate minerals include calcite, aragonite, and dolomite.
Dolomite is formed primarily through a geological process called dolomitization, where magnesium-rich fluids gradually replace calcium ions in limestone or calcareous mudstone. This process results in the formation of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of dolomite.
"Hydrated Dolomite" is a misnomer. The description provided refers to a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, not a hydrated form of the dolomite mineral CaMg(CO₃)₂. The formula (OH)CaMg is incorrect for hydrated dolomite; it suggests a compound that doesn't exist in nature or as a typical industrial product. A true hydrated dolomite would involve water molecules incorporated into the crystal structure of the dolomite mineral.
Chamotte is a refractory material made from calcined and crushed clay. It's essentially a byproduct of the refractory brick manufacturing process. The clay used in chamotte production typically has fewer impurities than the clay used for other ceramic products. Chamotte is a versatile and essential raw material widely used in various industries, particularly in ceramics and refractories.

- Address: Centeral Office : No 328 ,30 Alley, Mosala Street, Esfahan - Iran
- Tel :+983136617540
- Fax :+983136617541
- Email : info@azarsepeed.com
- Sales Email: commercial@azarsepeed.com

 FA
FA  EN
EN  AR
AR 





