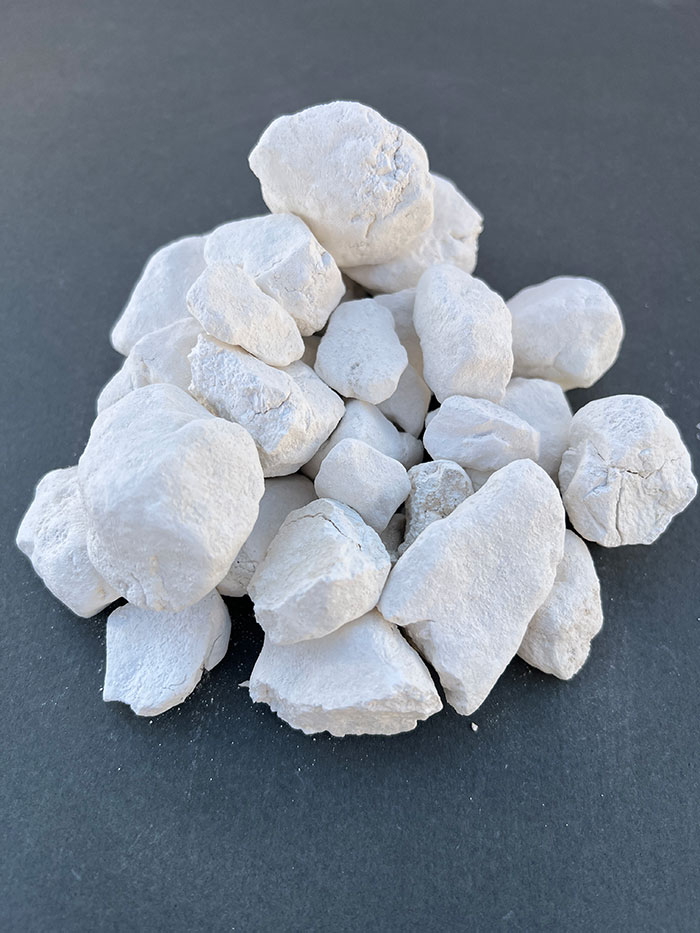
Calcined lime (burnt lime) is produced by calcining limestone (CaCO3). Calcination is the process of removing CO2 from limestone. Heating limestone to approximately 1200°C yields calcium oxide, also known as quicklime (CaO). In domestic production, less than 3 million tons of limestone are used in the metallurgical industry, with about half consumed in steel production.
Calcined lime is a crucial fluxing agent in steelmaking. However, lime used in the steel industry must have the highest possible CaO purity and minimal impurities such as SiO2, sulfur, and phosphorus.
analysis :
Chemical analysis Calcined Lime table
|
Grain Size(mm)
|
Bulk Density (gr/cm3) |
L.O.I |
AL2O3
|
Fe2O3 |
CaO
|
SiO2 |
MgO |
Chemical Analysis(%) Brand |
Product Name |
|
0 - 50 |
0.9 – 1.5 |
1 – 3 |
0.1 – 0.3 |
0.3 – 0.5 |
93 -97 |
0.6 – 1.3 |
0.5 – 1.5 |
AZ.C.L.L (Lime) |
Calcined |
Applications:
- Construction Industry:
- Used in cement production and as a component in lime and gypsum mortars.
- Metallurgy:
- Acts as a flux in steelmaking to remove impurities and is used in non-ferrous metal refining.
- Chemical Industry:
- Serves as a raw material in the production of various chemicals and for pH control in chemical processes.
- Water Treatment:
- Used for water softening and pH adjustment in treatment plants.
- Environmental Applications:
- Used in flue gas desulfurization to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions and in soil stabilization to improve soil properties.
- Agriculture:
- Corrects soil acidity and serves as a calcium supplement in animal feed.
- Food Industry:
- Used in food processing for water treatment and as a clarifying agent.

 FA
FA  EN
EN  AR
AR 
